Posted on April 6, 2020
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Jacksonville District opens public comment on the Draft Environmental Assessment (EA) and proposed Finding of No Significant Impact (FONSI) regarding potential sand sources for the renourishment of the Bal Harbour Beach segment of the Dade County Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project. Public comments will be accepted through May 4, 2020.
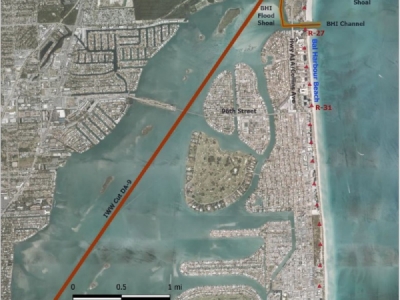
The Draft EA evaluates the use of additional sand sources for renourishment of Bal Harbour Beach, including dredged material from the Bakers Haulover Inlet (BHI) Channel and the Bakers Haulover Inlet Flood Shoal located between the federal channel of the Intracoastal Waterway and the Bakers Haulover Inlet Channel, and incorporates by reference the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) analysis that was completed by the Corps Regulatory Division for the Cemex and Garcia upland mine sources. Potential borrow area alternatives for the Bal Harbour Beach renourishment evaluated in previous EAs/FONSIs, identified as “existing sources,” include the Intracoastal Waterway Cut DA-9, the Bakers Haulover Inlet Ebb Shoal offshore in the Atlantic Ocean, and upland sand mines, including the Ortona and Witherspoon mines in Glades County. The potential for beneficial use of dredged material from the Bakers Haulover Inlet Channel and Bakers Haulover Inlet Flood Shoal, as well upland beach-quality sand will provide the Corps with additional options and flexibility, which is expected to reduce the overall cost of the beach renourishment project. In addition, the Bakers Haulover Inlet Channel is in need of maintenance dredging to provide safe and efficient travel for navigation interests.
The Preferred Alternative consists of renourishment of Bal Harbour using sand from existing sources, in addition to sand dredged from the Bakers Haulover Inlet Channel and Flood Shoal, as well as two additional upland sand mines, Garcia and Cemex.
The proposed project would renourish Bal Harbour Beach from the south jetty of Bakers Haulover Inlet south for 0.85 mile. The renourishment would help manage coastal storm risk and beach erosion and help provide hurricane surge protection. Beach erosion control benefits include protection of infrastructure, environmental preservation for wildlife, support for the economy (tourism), increased recreational value, and added coastal resiliency.
The Draft EA and proposed FONSI for the evaluation of additional sand sources for the Bal Harbour Beach segment of the Dade County Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project are available for review at the Bal Harbour Project page at www.saj.usace.army.mil/BalHarbour.
The Corps will accept written comments through May 4, 2020 via email to Kristen.L.Donofrio@usace.army.mil (recommended subject line: “Bal Harbour Draft EA Comments”).
Bal Harbour beach was most recently renourished in 2014 with 236,000 cubic yards of sand dredged from the Bakers Haulover Inlet Ebb Shoal offshore.
Bal Harbour Beach is included in the 10.5-mile Main Segment of the Dade County Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project for Dade County, Florida, authorized by the Flood Control Act of 1968 (Public Law 90-483). The Main Segment of the Dade County Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project extends from Government Cut in the south to Haulover Beach Park, just north of Dade County Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project.
This renourishment project is 100 percent federally funded via the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (Public Law 115-123).
The Corps is the federal agency responsible for maintaining the authorized project width and depth for the Intracoastal Waterway. The Intracoastal Waterway from Jacksonville to Miami was originally authorized to by the Flood Control Act of 1927. The Bakers Haulover Inlet Channel was authorized by the Flood Control Act of 1960 (Public Law 86-645).
For additional information, visit the Bal Harbour Project page at www.saj.usace.army.mil/BalHarbour.
Contact
Erica Skolte
561-801-5734 (cell)
Erica.A.Skolte@usace.army.mil
Source: usace.army.mil





